-
About Us
button

Dabur India Limited is a leading Indian consumer goods company with interests in Hair Care, Oral Care, Health Care, Skin Care, Home Care and Food & Beverages.
-
Our Brands
button

Dabur presents a range of Herbal & Ayurvedic Personal Care products, created to make you look and feel good. Bringing together the gentle touch of nature and Ayurveda's wisdom .
-
Investors
button

Read our recent and archived releases, quarterly results, annual reports and financial statements. Initiatives Investor Centre.
-
Newsroom
button

Welcome to Dabur Media Centre. In this section, you’ll find our latest Press Releases arranged in a chronological order. The Press Releases have been further
-
Ayurveda & you
button

Our curated Collection of Ayurvedic knowledge for you. We at Dabur are working towards helping people lead a healthy and balanced life.
-
Sustainability
button
Dabur has been engaged in community development activities since 1994 and is committed to making a positive contribution to the communities where we source, live, work and sell our products.
-
Join Us
button

At Dabur, we are very passionate about winning and this has been engrained in DNA of the organization.
-
Support
button
- Home > Ayurveda & you > Ayurveda & Science > Ayurvedic & Medicinal Plants
Ayurveda and Science
Ulatkambal/उलाटकमबल/Abroma augusta/Devil’s Cotton/Pishach Karpas
AYURVEDIC & MEDICINAL PLANTS

The leaves and stems are covered with soft bristly hairs that are very irritating to the touch. The bark yields a jute-like fiber. In the greenhouse, plants bloom from late spring to early summer. Dark maroon flowers are formed in terminal panicles. Individual flowers are up to 3 inches (7.5 cm) across
Abroma Augusta Medicinal Uses
Devil’s cotton is a uterine stimulant and is specifically indicated in amenorrhoea and oligomenorrhea as recommended by Indian Ayurveda. Due to its pain relieving activity it is also given in Dysmenorrhoea. It is given three days prior to the onset of menses and is continued till the second day of the cycle.
Chemical Composition
The main constituents of Abroma augsta include Tannins, magnesium, fixed oil and alkaloids.
Pacifies vata and kapha and increases pitta.
Read more about various ailments, it's causes, symptoms, ayurvedic treatments, etc.
Know the story behind other medicinal Ayurvedic ingredients
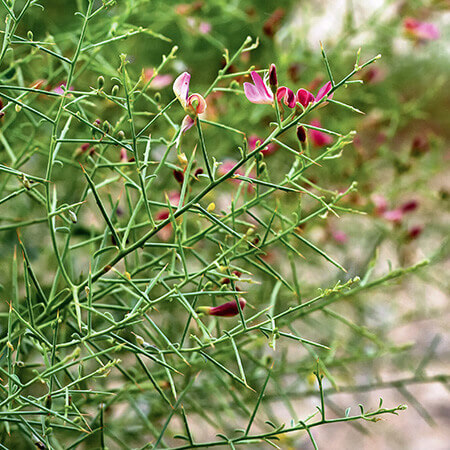

Yavasa
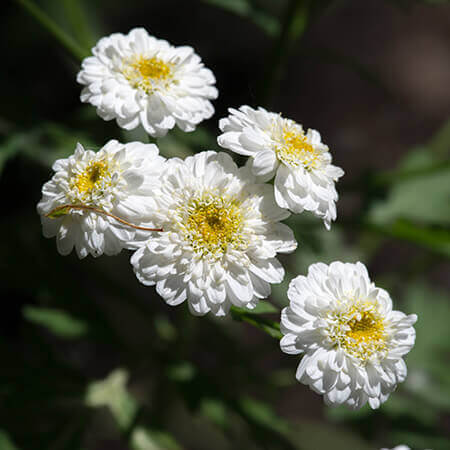

Akarkara
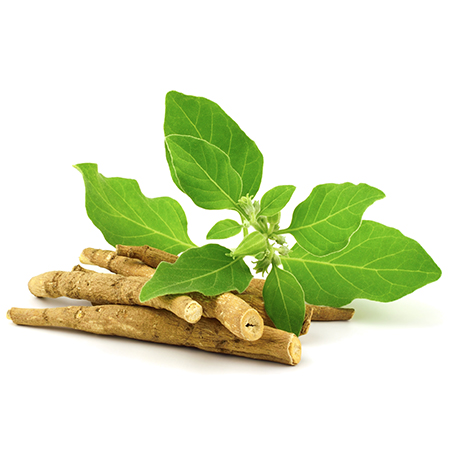

Ashwagandha
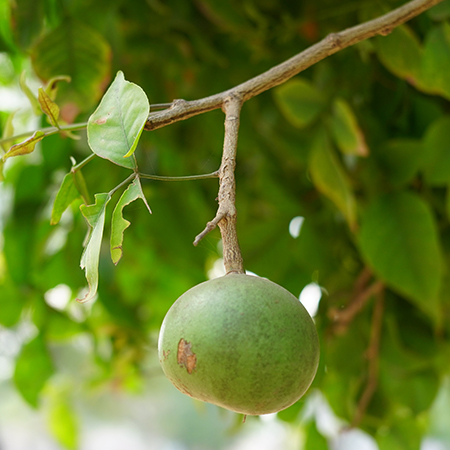

Bael



